As a leading healthcare provider, Paarvati Devi Hospital understands the importance of managing diabetes effectively for maintaining overall health and well-being. With the rising prevalence of diabetes worldwide, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of this chronic condition and adopt a healthy lifestyle to manage it effectively. In this blog post, we will provide a guide to managing diabetes, including its types, causes, symptoms, and essential tips for leading a healthy lifestyle.
Types of Diabetes:
Diabetes is classified into three main types:
Type 1 Diabetes: This type occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It is usually diagnosed in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin injections for management.
Type 2 Diabetes: This type is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body does not effectively use insulin or does not produce enough insulin. It is commonly associated with risk factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history, and age. Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes insulin.
Gestational Diabetes: This type occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes affect insulin sensitivity. It usually resolves after delivery, but it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact causes of diabetes are not fully understood, but several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition, including:
Genetics: Family history of diabetes can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle factors: Sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, obesity, and lack of physical activity can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after 45 years.
Gestational factors: Women who have had gestational diabetes or have given birth to a baby weighing over 9 pounds are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Ethnicity: Certain ethnicities, such as African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asians, have a higher risk of developing diabetes.
Common Symptoms:
The symptoms of diabetes may vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms of diabetes may include:
Frequent urination
Increased thirst and hunger
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue and weakness
Blurred vision
Slow healing of wounds or infections
Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
It's important to note that some people with type 2 diabetes may not experience any symptoms, and the condition may be diagnosed during routine health checkups or screenings.
Essential Tips for Managing Diabetes:
Managing diabetes requires a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, medication (if prescribed), regular monitoring, and medical care. Here are some essential tips for managing diabetes and leading a healthy lifestyle:
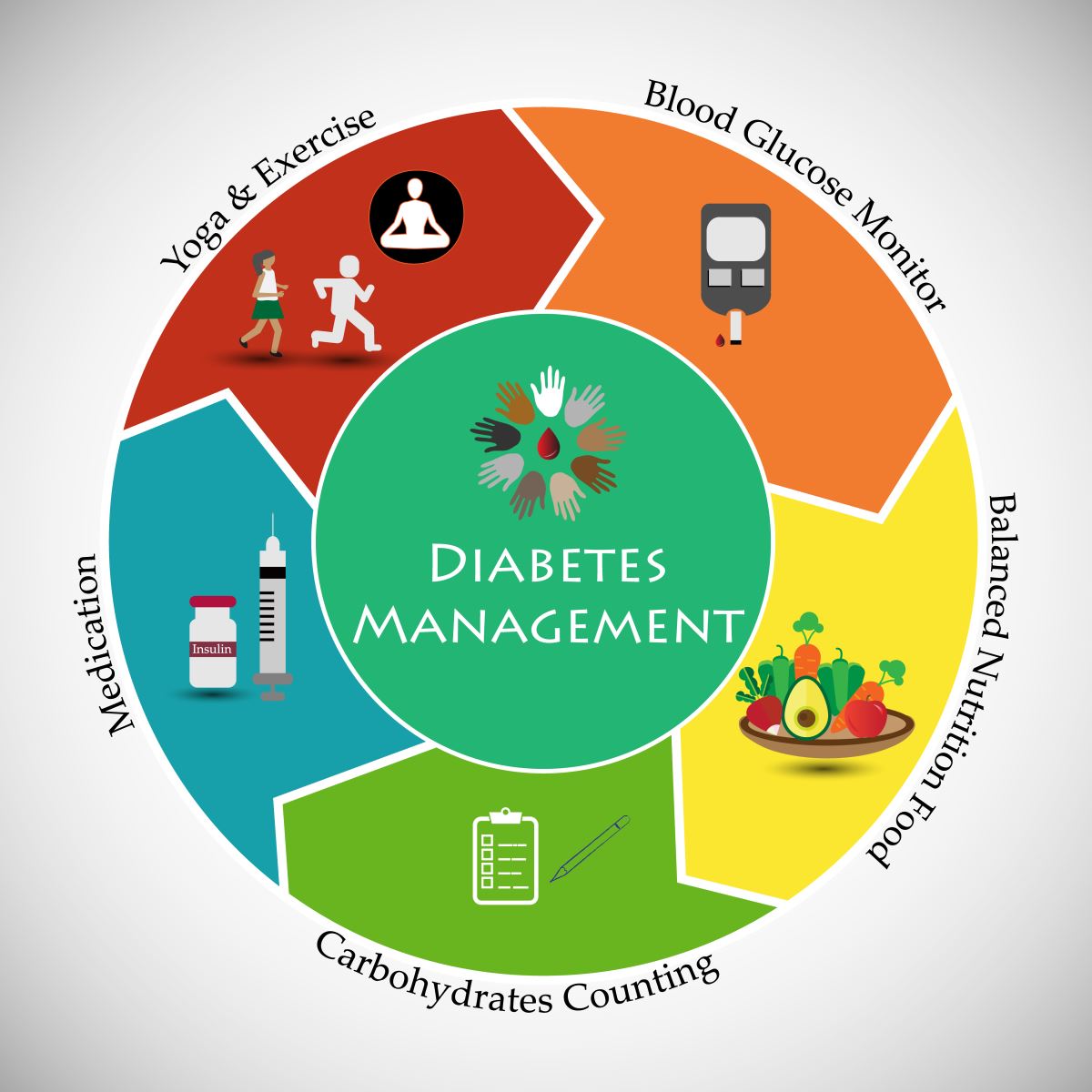
Follow a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is crucial for managing diabetes. Avoid sugary foods, processed foods, and excessive consumption of carbohydrates. Consult a registered dietitian for personalized meal planning.
Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, per week, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider. Keep a record of your readings and share them with your healthcare team for proper management.
Take medications as prescribed: If you are prescribed medication for diabetes, take them as instructed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip doses or stop medications without consulting your healthcare team.
Types of Diabetes:
Diabetes is classified into three main types:
Type 1 Diabetes: This type occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It is usually diagnosed in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin injections for management.
Type 2 Diabetes: This type is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body does not effectively use insulin or does not produce enough insulin. It is commonly associated with risk factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history, and age. Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes insulin.
Gestational Diabetes: This type occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes affect insulin sensitivity. It usually resolves after delivery, but it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact causes of diabetes are not fully understood, but several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition, including:
Genetics: Family history of diabetes can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle factors: Sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, obesity, and lack of physical activity can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after 45 years.
Gestational factors: Women who have had gestational diabetes or have given birth to a baby weighing over 9 pounds are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Ethnicity: Certain ethnicities, such as African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asians, have a higher risk of developing diabetes.
Common Symptoms:
The symptoms of diabetes may vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms of diabetes may include:
Frequent urination
Increased thirst and hunger
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue and weakness
Blurred vision
Slow healing of wounds or infections
Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
It's important to note that some people with type 2 diabetes may not experience any symptoms, and the condition may be diagnosed during routine health checkups or screenings.
Essential Tips for Managing Diabetes:
Managing diabetes requires a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, medication (if prescribed), regular monitoring, and medical care. Here are some essential tips for managing diabetes and leading a healthy lifestyle:
Follow a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is crucial for managing diabetes. Avoid sugary foods, processed foods, and excessive consumption of carbohydrates. Consult a registered dietitian for personalized meal planning.
Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, per week, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider. Keep a record of your readings and share them with your healthcare team for proper management.
Take medications as prescribed: If you are prescribed medication for diabetes, take them as instructed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip doses or stop medications without consulting your healthcare team.
